(Biology) ICSE Class X Important Questions : Biology (2000)
Disclaimer: This website is NOT associated with CBSE, for official website of CBSE visit - www.cbse.gov.in
Paper : ICSE Class X Important Questions : Biology (2000)
General Instrutions
- Attempt all questions from Section I and any four questions from Section II.
- The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in brackets.
SECTION I (40 Marks)
Compulsory: Answer all parts from this Section.
Questions 1
(a) Name the following: [8]
- The organ which produces urea.
- The iron containing pigment in Erythrocytes.
- The junction between two nerve cells.
- The phase of the cardiac cycle in which the auricles contract.
- An apparatus to compare the rate of transpiration in cut shoots.
- The pressure exerted by cell contents on a plant cell wall.
- The fluid surrounding the developing embryo.
- The outer part of the kidney containing the Bowman's capsules.
(b) Select the correct answer out of the four available choices given under each question. [8]
- The space between the cell wall and plasma membrane in plasmolysed cell is
filled with:
(i) isotonic solution
(ii) hypotonic solution
(iii) hypertonic solution
(iv) water - In the process of respiration: (i) ADP is converted to ATP. (ii) glucose is converted to carbon dioxide. (iii) glucose is converted to carbon dioxide and water, releasing energy. (iv) pyruvic acid is converted to ATP.
- Which of the following gland has both endocrine and exocrine functions?
(i) pituitary gland
(ii) thyroid gland
(iii) pancreas gland
(iv) adrenal gland - During inspiration, the diaphragm:
( i) relaxes
(ii) contracts
(iii) expands
(iv) does not change - The specnic function of light energy in the process of photosynthesis to:
(i) reduce carbon dioxide
(ii) synthesise glucose
(iii) activate chlorophyll
(iv) split water - The chief function of lymph nodes in mammals is to:
(i) produce WBC's
(ii) produce hormones
(iii)destroy old RBC's (
iv) destroy pathogen. - Agranulocytes are
(i) lymphocytes, monocytes
(ii) lymphocytes, basophils.
(iii) eosinophils, basophils
(iv) eosinophils, monocytes. - Sterilization in the females involves cutting and tying the:
(i) ureter
(ii) uterus
(iii) urethra
(iv) oviduct
(c) Given below is an example of a certain structure and its special functional activity, e.g. kidney and excretion. On a similar pattern fill in the blanks. [8]
- Mitochondria and .........................
- Erythrocyte and ...........................
- Glomerulus and .................................
- Cerebellum and .....................
- Larynx and .................
- Corpus luteum and ...................
- Myelin sheath and .....................
- Organ of corti and .................
(d) Choose the odd one in each of the following series: Example : Calyx; Corolla; Style; Androecium. Answer: Style. [8]
- Ovary; Fallopian tube; Ureter; Uterus.
- Myopia; Hypermetropia; Xerophthalmia; Astigmatism.
- Cholera, Whooping cough; Diphtheria; Measles.
- Glomerulus; Alveolus; Bronchus; Trachea.
- Thyroid gland; Adrenal gland; Pituitary gland; Prostrate gland.
- Cretinism; Myxoedema: Goitre; Scurvy.
- Insulin; Glucagon; Diabetes insipidus; Diabetes mellitus.
- Pons; Cerebellum; Medulla Oblongata; Cerebrum.
(e) Match the terms of column I with those of column II and write down the matching pairs: [6]
| COLUMN I | COLUMN II |
| (i) Bowman's capsule (ii) Dendrons (iii) Acrosome (iv) Iris (v) Ovulation (vi) Pacemaker (vii) Pleura (viii) Nephrons |
(a) Spermatozoa (b) Kidney tubules (c) S.A. Node (d) A.V Node (e) Glomerularfiltration (f) Lungs (g) Nerve impulse (h) Testis (i) Colour of eye (j) Oxytocin (k) Luteinizing hormone (l) Progesterone |
SECTION II (40 Marks)
Answer any four questions from this section.
Question 2
(a) Given below is a simple diagram of the circulation of blood in a mammal
showing the main blood vessels, the heart, lungs and body tissues. The blood
vessel labelled 6 contains deoxygenated blood and the valve leading to it has
three semi-lunar pockets. [5]
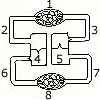
- Name the blood vessels or organs marked by numbers 1 to 8.
- What do you mean by 'double circulation' of blood in mammals?
- What is diastole?
(b) Note the relationship between the first two words and suggest the suitable word/words for the fourth place. [5]
- Thylakoid : Chloroplast: : Cristae :..........................
- Cones : Iodopsin : Rods :...................
- Stomata : Transpiration : Hydathodes : ...................
- Lubb : Atrioventricular valves : Dup : ....................
- Coronary artery : Heart Hepatic artery : ....................
Question 3 [5]
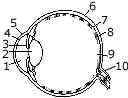
(a) The diagram given below refers to the vertical section of the eye of a mammal. Label the parts 1 to 10 to which the guideline points.
(b) The following diagram refers to an apparatus which is used to demonstrate a physiological process. [5]
- What is the purpose of keeping potassium hydroxide solution in test tubes X and Y?
- What is the purpose of keeping boiled peas soaked in a disinfectant in test tube Y?
- Why has coloured water risen in tubing 1?
- Name the biological process which causes the above rise.
- Define the biological process shown in the experiment.
Question 4
(a) The volume of air in the lungs and the rate at which it is exchanged during
inspiration and expiration is measured with a spirometer. The following diagrams
shows the spirogram of lung volumes and capacities. Study the graph carefully
and explain briefly the following: [5]
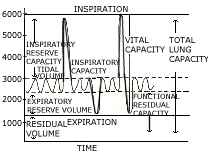
- Tidal volume (TV)
- Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV).
- Expiratory reserve volume (ERV).
- Vital capacity (VC).
- Residual volume (RV)
(b) The following diagram is a set up to demonstrate an experiment. Pondweed was placed in five water filled tubes. The experiment was set up as shown in the diagram. The tubes were then left for 24 hours. Write the correct answer out of the available choices given under each question.
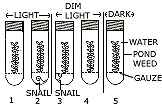
- In which tube would you expect the greatest increase in dry weight of the
pondweed?
(i) l (ii) 2 (iii) 3 (iv) 4 (v) 5 - In which tube would you expect to find the plant with the least amount of
starch?
(i) 1 (ii) 2 (iii) 3 (iv) 4 (v) 5 - The tube in which most oxygen would be fiind is:
(i) 1 (ii) 2 (iii) 3 (iv) 4 (v) 5 - The tube in which least carbon dioxide would be find is:
(i) 1 (ii) 2 (iii) 3 (iv) 4 (v) 5 - The tube in which the plant would survive for the shortest length of time
is:
(i) 1 (ii) 2 (iii) 3 (iv) 4 (v) 5
Question 5
(a) The following diagram represents the vertical view of 5 gm the female
reproductive system. [5]
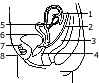
- Label the part indicated by the guidelines 1 to 8.
- How does the uterus prepare for the reception of zygote?
- What happens to the uterus if fertilization takes place?
- What happens to the uterus if fertilization has failed to take place?
(b) The given diagram refers to an experiment in which the apparatus was set up with light source 10 cm away from the plant. After 15 minutes the number of bubbles evolved per minute from the cut stem was recorded. The light source was moved to 20 cm away from the plant for 15 minutes and the number of bubbles evolved per minute was again recorded. The experiment was repeated with the source of light at distances of 40, 60, 80 and 100 cm away from the plant. The result obtained were recorded on the graph. Select the correct answer out of the available choices given under each question. [5]
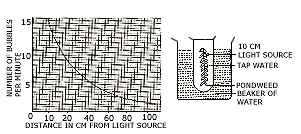
- From the graph it seems likely that the rate of bubbling per minute at 50
cm would have been:
(i) 2.0 (ii) 2.5 (iii) 3.0 (iv) 3.5 (v) 4.0 - The gas produced by the plant during the experiment was
(i) air (ii) oxygen
(iii) carbon dioxide (iv) nitrogen
(v) hydrogen - The gas collected comes due to the breakdown of:
(i) glucose (ii) starch
(iii) water (iv) air
(v) ATP - If ice cubes were added to the water the rate of bubble formation would:
(i) stay the same.
(ii) increase because more water is added. (iii) decrease because the temperature drops. (iv) decrease because water freezes. (v) cannot tell from the information given. - If some sodium bicarbonate is added to the water the rate of bubble
formation: (i) increases because more respiration occurs. (ii) increases
because more photosynthesis occurs. (iii) increases because the gas becomes
less soluble. (iv) decreases because carbon dioxide acts as a limiting
factor.
(v) decreases because respiration occurs
Question 6
(a) The given diagram refers to the ear of a mammal. [5]
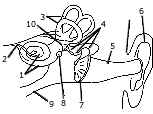
- Label the parts 1 to 10 to which the guidelines point.
- Which structure.
(1) Converts sound waves into mechanical vibrations?
(2) Converts vibrations into nerve impulses?
(3) Responds to change in position? (4) Transmits impulses to the brain? (5) Equalizes atmospheric pressure and pressure in the ear?
(b) Complete the following statements by choosing the correct alternative from the choices given in brackets. [5]
- (Myxoedema/simple goitre/exophthalmic goitre) is a disorder caused by excess thyroid hormone.
- The (epididymis/vas deferens/seminal vesicle) stores sperms.
- The dorsal root ganglion of the spinal cord contains cell bodies of (motoe/sensory/intermediate) neurons.
- The (alveoli/bronchioles/tracheoles) are the ultimate end parts of the respiratory system in man.
- Write the blood cells engulf bacteria in a process called (diapedesis phagocytosis/active transport)
Question 7
(a) The apparatus shown here is Garreau's potometer designed to demonstrate
unequal transpiration from the two surfaces of a dorsiventral leaf. Before
keeping the leaf in between the cups, anhydrous calcium chloride (CaCl2)
contained in two small vials were weighed and placed in both the cups. The ends
of the cups were closed with corks through which two mercury manometers were
connected. After few hours, CaCl2 vials were taken out and weighed again. [4]
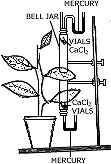
- What is the purpose of keeping CaCl2 vials inside the cup?
- After a few hours, CaCl2 vials were taken out and weighed again. Will you expect any difference in weight? If so give reason.
- What was the purpose of using a manometer?
- What do you mean by transpiration?
(b) The diagram given below refers to the following account of an investigation and a graph of the results obtained.In 1986 a large city experienced a dense fog from 4th to 9th December. During this time there was an increase in the number of deaths. In answering the following questions use the graph which show how deaths per day were related to the amount of sulphur dioxide in the air. Select the best answer out of the five available choices given under each question. [6]
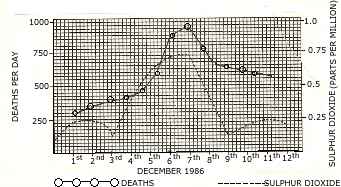
- On which clay was the increase in sulphur dioxide greatest?
(i) 4th December
(ii) 5 th December
(iii) 6th December
(iv) 7th December
(v) 8th December
- How many deaths occurred on the day following the highest sulphur dioxide
concentration ?
(i) 350
(ii) 575
(iii) 700
(iv) 875
(v) 925
- The graph shows the deaths per day were not:
(i) lower before the fog than during the fog.
(ii) higher after the fog than before fog.
(iii) highest at the time of fog.
(iv) decreasing after fog.
(v) increasing throughout the fog.
- Clean air prevents the occurrence of fog. Which of the following will help
to ensure a clean environment.
(i) air pollution
(ii) education
(iii) legislation
(iv) population control
(v) ventilation