(Biology) ICSE Class X Important Questions : Biology (2002)
Disclaimer: This website is NOT associated with CBSE, for official website of CBSE visit - www.cbse.gov.in
Paper : ICSE Class X Important Questions : Biology (2002)
General Instructions
-
Attempt all questions from Section I and any four questions from Section II.
-
The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in brackets.
SECTION I (40
Marks)
Attempt all questions from this Section.
Question 1
(a) Name the following: [8]
-
A substance that initiates an immune response.
-
A fluid that transports fatty acid and glycerol.
-
The structure in which the testes are present in a man.
-
The micro-organism that causes AIDS.
-
The valve present in between the chambers of the right side of the human heart.
-
Condition of a cell placed in hypotonic solution.
-
A pollutant largely responsible for acid rain.
-
The part of the human brain that controls body temperature.
(b) Given below are certain functional activities of specmc structures in the body of living organisms. Name the structure responsible for the same. [8]
-
Prevents food from entering the trachea during swallowing.
-
Transfers impulses from inner ear to brain.
-
Initiates cell division in animal cells.
-
Helps to change the focal length of the eye lens.
-
Transports oxygen to the cells of the human body.
-
Helps to increase the volume of the chest cavity lengthwise.
-
Transports manufactured food from leaves to other parts of the plan.
-
Acts as bearer of heredity units.
(c) Choose the correct answer to the
following:
(You may either write the statement with the correct answer or may write the
corresponding letter of the alphabet.) [8]
-
Cerebellum is the part of the brain which is responsible for:
(a) Interpreting sensations.
(b) Conducting reflexes in the body.
(c) Maintaining posture and equilibrium.
(d) Controlling thinking, memory and reasoning. -
The mineral element essential for the clotting of blood is:
(a) Iron.
(b) Calcium.
(c) Iodine.
(d) Sulphur. -
A plant is kept in a dark cupboard for about 48 hours before conducting any experiment on photosynthesis to:
(a) Remove chlorophyll from the leaves.
(b) Remove starch from the plant.
(c) Ensure that no photosynthesis occurs.
(d) Ensure that the leaves are free from starch. -
The parts of the human ear concerned with hearing are: (a) Cochlea, ear ossicles and tympanum.
(b) Semicircular canals, utricules and saccules.
(c) Eustachian tube, tympanum and utricules.
(d) Perilymph, ear ossicles and semicircular canals. -
During respiration, there is:
(a) Gain in dry weight.
(b) Loss in dry weight.
(c) No change in weight.
(d) All of the above depending on the type of respirable material. -
Marine fish when thrown under tap water bursts because of: (a) Endosmosis
(b) Exosmosis
(c) Diffusion
(d) Plasmolysis -
Introduction of deadened or weak microbes into the body is termed:
(a) Immunisation
(b) Vaccine
(c) Sterilisation
(d) Vaccination -
Duplicated chromosomes are joined at a point termed :**
(a) Centrosome
(b) Centromere
(c) Centriole
(d) Chromatid
(d) Match the items in Column I with those which are most appropriate in Column II. You must rewrite the matching pairs: [8]
|
COLUMN I |
COLUMN II |
|
(a) Liver |
(i) basic unit of the brain |
(e) Given below is a table consisting of a set of items belonging to a common category. Complete the table by filling in the category and the odd one in the blanks. The first example has been done for you. [8]
|
SET |
CATEGORY |
ODD ONE |
|
(i) Glucose, Starch, Cellulose, Calcium |
Carbohydrates |
Calcium |
Section - II
(40 marks)
Answer any four questions from this section.
Question 2
(a) The following diagram represents the human brain as
seen in an external view. Study the same and then answer the questions that
follow: [6]
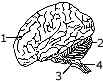
-
Name the parts labelled 1,2,3 and 4.
-
Mention the difference in the arrangement of the nerve cells in the parts marked '1' and '4'.
-
What is the main function of the parts marked '3' and '4'?
-
Name the sheet of nerve fibres that connect the two halves of the part labelled '1'.
(b) Define the following terms: [4]
-
Photophosphorylation
-
Diffusion
-
Noise pollution
-
Synapse.
Question 3
(a) The figure given alongside is a diagrammatic representation of a part of
cross section of the root hair zone.Study the same and then answer the questions
that follow: [6]
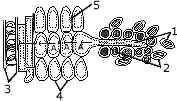
-
Name the parts indicated by guidelines '1' to '5'
-
Is the root hair cell unicellular or multi-cellular?
-
Draw a labelled diagram of the root hair cell as it would appear if some fertilizer is added to the soil close to it.
-
Name the process responsible for the entry of water molecules from the soil into A1 and then A 2.
-
What pressure is responsible for the movement of water in the direction indicated by arrows?
-
How is this pressure set up?
(b) Mention the difference between the following pairs on the basis of what is given in brackets: [4]
-
Artery and Vein (Type of blood flowing through)
-
Serum and Vaccine (Composition)
-
Antiseptic and Disinfectant (Function)
-
Photosynthesis and Respiration (Reactants).
Question 4
(a) The diagram given alongside is that of a developing human foetus in the
womb. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow: [6]
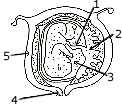
-
Name the parts '1' to '5' indicated by guidelines.
-
What term is given to the period of development of the foetus in the womb?
-
How many days does the foetus take to be fully developed? (iv) Mention two functions of the parts labelled '2' other than its endocrine function.
-
Name the hormone (any one) produced by the part labelled '2'.
-
What is the function of the part marked '3'?
(b) [4]
-
State Mendel's law of dominance.**
-
What is a dihybrid ratio?**
-
Define Phenotype.**
-
What are Autosomes?**
Question 5
(a [6]
-
What is a Lacrimal gland?
-
In what two ways is yellow spot different from blind spot?
-
Name an old-age eye defect. Why is it caused?
-
What is meant by 'power of accommodation of the eye'?
-
Mention the characteristics of the image that falls on the retina of the eye.
-
Name the photoreceptors found in the retina of the eye.
(b) In each of the following cases, pick out one term which includes the other three: [4]
-
glucose, oxygen, energy, oxidation.
-
(glomerular filtrate, bowman’s capsule, ultrafiltration, glomerulus.
-
ethyl alcohol, carbon dioxide, anaerobic, oxygen absence.
-
diffusion, respiratory gases, alveoli, capillary network.
Question 6
(a) In order to study and prove a particular physiological process in plants,
the following experiment was set up. Study the same and then answer the
questions that follow: [6]
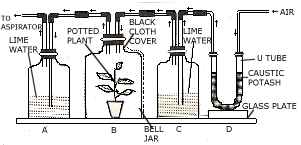
-
Name the physiological process being studied.
-
What is the function of soda lime in the bottle 'A' and why is lime water placed in bottle 'B'?
-
What change would you expect to observe in bottle 'D'?
-
Represent the physiological process named in (i) above in the form of a chemical equation.
-
In order to obtain accurate results, the bottle 'C' should be covered with a .black cloth. Why?
-
In bottle 'C' were fitted with a 3 holed rubber stopper and a thermometer were introduced in such a way that its bulb reaches close to the germinating seeds, what would you observe? Why?
(b) Column 'B' is a list of items related to ideas in Column 'A' Match the term in Column ‘B’ with the suitable idea given in Column 'A' [6]
|
Column A |
Column B |
|
(i) Chromosomes become arranged in a
horizontal plane at the equator. |
Anaphase |
Question 7
(a) Given below is diagram of a smear of human blood. Study the same and then
answer the questions that follow: [6]
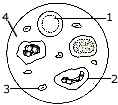
-
Name the parts 1, 2, 3 and 4 indicated by guidelines.
-
Mention two structural differences between the parts labelled '1' and '2'.
-
What is the main function of the parts labelled 1, 2, 3?
-
What is the life span of the part labelled '1'?
-
Name a soluble protein found in '4' which helps in the clotting of blood.
-
Name the disease in which blood fails to clot naturally.
(b) What do the following abbreviations stand for: [4]
-
WHO
-
NADP
-
DNA
-
ATP