(Physics) ICSE Class X Important Questions : Physics (1998)
Disclaimer: This website is NOT associated with CBSE, for official website of CBSE visit - www.cbse.gov.in
Paper : ICSE Class X Important Questions : Physics (1998)
General Instructions
-
Attempt all questions from Section I and any four questions from Section II.
-
The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in brackets.
SECTION I (40
Marks)
Attempt all questions from this Section.
Question 1
(a) [4]
-
What is the S.I. unit of work?
-
A body of mass 1 kg falls from a height of 5 m. How much energy does it possess at any instant, (take g = 9·8 m/s2)?
-
When a body moves in a circular path how much work does it do?
(b) The diagram alongwith shows the use of a lever. [4]
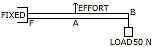
-
State the principle of moments as applied to the lever.
-
Give an example of this class of lever.
-
If FA = 10 cm, AB = 500 cm, calculate the minimum effort required to lift the load.
(c) [4]
-
State Archimede's Principle.
-
A man first swims in sea water and then in river water.
a. Compare the weight of sea water and river water displaced by him.
b. Where does he find it easier to swim and why?
(d) [4]
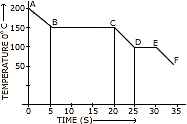
-
The graph alongside represents a cooling curve for a substance being cooled from a higher temperature to a lower temperature.
a. What is the boiling point of the substance?
b. What happens in the region DE?
c. Why is the region DE shorter than the region BC? -
At what approximate temperature will water boil in a pressure cooker?
(e) The diagram shows a ray of white light AO incident on a rectangular glass block, which is silvered at one surface. This ray is partly reflected and partly refracted. [4]
-
Copy the diagram and trace the path of the refracted and reflected ray. Show at least two rays emerging out from the surface PQ.
-
How many images are formed in the above case? Which image is the brightest?
(f') The diagram alongside shows a student's vision from his near point. [4]
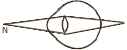
-
What defect is he suffering from?
-
State one cause for the occurrence of this defect.
-
Copy the diagram and complete it to show how this defect is corrected.
(g) [4]
-
The alongside diagram shows two straight wires carrying current. Copy |the diagram and draw the pattern of lines of force around them and mark their directions.
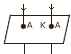
-
How is a galvanometer converted to
a. An ammeter
b. A voltmeter?
(h) [4]
-
A refrigerator is marked 80 W and 220 V. 1. How much energy does it consume in one day if on an average it is used for 20 hrs. a day? 2. What is likely to happen if the voltage drops to 50 V?
-
Score off the incorrect words and write correctly the following: In wiring a three pin plug, the brown sleeved wire is connected to the neutral/live pin and the green/blue sleeved wire is connected to the metal body of the appliance.
(i) X-rays are produced in a coolidge tube when cathode rays are made to strike a target. [4]
-
Why is the anode of the tube heated up at the time of emission of X-rays?
-
How are the strength and penetrating power controlled?
-
Which of the soft and hard X- rays has a longer wavelength and which has higher penetrating power?
(j) [4]
-
State the transformation of energy taking place in a :1. Loud speaker 2. Washing machine.
-
An α-particle absorbs an electron. What does it change to?
-
A fusion reaction is represented as follows:
|
|
H + |
|
H→ |
|
He + x. |
SECTION - II
(40 Marks)
Attempt any four questions from this Section.
Question 2
(a) A bullet of mass 50 g is moving with a velocity of 500 m/s. It penetrates 10
cm into still target and comes to rest. [3]
-
Calculate the kinetic energy possessed by the bullet.
-
The average retarding force offered by the target.
(b) The diagram alongside shows a system of 5 pulleys. [3]
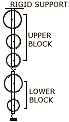
-
Copy the diagram and complete it by drawing a string around the pulleys. Mark the position of load and the effort.
-
If the load is raised by 1 m, through what distance will the effort move?
(c) A flat bottomed test tube floats upright with some lead shots on the surface of water with 10 cm of its length immersed. The test tube and lead shots are found to weigh 20 g when weighed in a beam balance. The same test tube when floated in kerosene was found to float with 12 cm immersed. [3]
-
What mass of water does it displace when floated on water?
-
What is the area of cross-section of the tube?
-
Calculate the R.D. of kerosene.
Question 3
(a) Explain, why bottled soft drinks are more effectively cooled by cubes of ice than by ice water? [5]
(b)10 g of ice at 00C absorbed 5,460 J of heat to melt and change into water at 500C. Calculate the specific latent heat of fusion of ice. [Specific heat capacity of water is 4,200 J/kg/0C]. [4]
(c) In an experiment to determine
the specific latent heat of vaporisation af steam L, the following measurements
were taken.
Mass of calorimeter + stirrer = x kg. Mass of water = y kg. Initial temperature
of water = t01,°C Final temperature of mixture = t2 °C
[Given : S.H.C., of calorimeter and water are S1 and S2
respectively]. Express in terms of above data. [4]
Question 4
(a) [4]
-
Differentiate between "forced vibrations" and "resonance".
-
How do the frequency and amplitudes affect a musical sound?
(b) Two musical notes of same pitch and loudness are played on a violin and a piano. The waveforms are as shown in figures alongside. Explain why the wave patterns are different. [2]
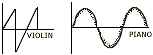
(c) [4]
-
An electromagnetic wave has afrequency of 500 MHz and a wavelength 60 cm. Calculate the velocity of the wave. Name the medium through which it is travelling.
-
A wave has a wavelength of 0.01 Å. Name the wave.
Question 5
(a) What is meant by: [2]
-
Critical angle;
-
Total internal reflection?
(b) [4]
-
Draw a diagram to show that white light can be split up into different colours.
-
Draw another diagram to show how the colours can be combined to give the effect of white light.
-
How would you show the presence of ultra-violet and infrared rays in the spectrum?
(c) When yellow paint and blue paint are mixed we get green colour. When yellow light and blue light are mixed white light is obtained. Give reasons for the observations mentioned. [2]
Question 6
(a) [3]
-
State Ohm's law.
-
State the factors that alter the resistance af a conductor.
(b) The alongside circuit diagram shows three resistance 2Ω, 4Ω and RΩ connected to a battery of emf 2V and internal resistance 3Ω. A main current of 0.25A flows through the circuit: [5]
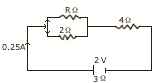
-
What is the P.D., across the 4Ω RΩ AΩ resistor?
-
Calculate the PD., across the internal resistance of the cell.
-
What is the PD., across the RΩ or the 29 resistors?
-
Calculate the value of R.
(c) State two ways of increasing the speed of rotation of a D.C. motor. [2]
(a) [5]
-
Draw a neat labelled diagram of a hot cathode ray tube.
-
What is the effect on the beam particles if: 1. A hotter filament is used. 2. the anode voltage is increased.
-
Name one device in which the cathode ray tube is used.
(b) State the factors that affect the rate of emission of electrons in a photoelectric cell. [2]
(c) [3]
-
A thorium isotope
233 Th
90
undergoes an α-decay and changes to radium. What are the atomic number and mass number of radium produced? -
If the radium undergoes a further disintegration and emits two β-particles, represent the reaction in the form of an equation.
-
What is the source of energy released during the decay?