(Physics) ICSE Class X Important Questions : Physics (2001)
Disclaimer: This website is NOT associated with CBSE, for official website of CBSE visit - www.cbse.gov.in
Paper : ICSE Class X Important Questions : Physics (2001)
General Instructions
- Attempt all questions from Section I and any four questions from Section II.
- The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in brackets .
SECTION I (40 Marks)
Attempt all questions from this Section.
Question 1
(a) [4]
- What is the weight of a body of mass 12 kg? What is the force acting on it? (g = 10m/s2)
- To use a machine as a force multiplier, what type (class) of lever should preferably be used? Draw a sketch of such a lever.
(b) [4]
- State if pressure at a point in a liquid is a vector or a scalar quantity.
- A block of wood is so weighted that it just floats in water in a jar at
room temperature.
a. If the water is now heated, what change will occur in the state of floatation of the block?
b. If the water in the jar is cooled to 4°C, what change will be observed in the state of floatation?
c. Give reasons for the above.
(c) In an optical camera state: [4]
- The nature of the lens used.
- What is meant by f-number?
- Two characteristics of the image formed by the lens.
(d) [4]
- Explain, why in day light an object appears red when seen through a red glass and black when seen through a blue glass?
- Name the extreme colours in pure spectrum of light.
(e) [4]
- Explain, why one feels ice-cream at 00C colder than water at 00C?
- Draw the diagram of the ring main circuit.
(f) [4]
- Give one example each. of natural vibration, forced vibration and resonance.
- Mention one practical use of echoes.
(g) Name the physical quantity that is measured in: [4]
- Kilowatt;
- Kilo-watt-hour,
- Light year and
- Hertz.
(h) [4]
- A family uses a light bulb of 100 W, a fan 0f 100 W, and a heater of 1000 W, each for 8 hours a day. If the cost of electricity is Rs. 2 per unit, what is the expenditure for the family per day, on electricity?
- How does earthing prevent electrical shock?
(i) [4]
- Name the particles given out during radioactive decay.
- Show by equations, the effect on the proton number Z and mass number A of the parent nucleus brought about by the two types of radioactive decay.
(j) [4]
- What is Carbon-14-dating?
- Given OC is equal to the focal length of the lens; copy the diagram in your answer book. Draw two rays from the linear object OO1, and obtain the image formed by the lens.
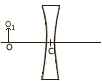
SECTION II
Attempt any four questions from this Section.
Question 2
(a) A pair of scissors and a pair of pliers belong to the same class of levers.
[3]
- Which one has mechanical advantage less than one?
- State the usefulness of a machine whose mechanical advantage is less than one.
(b) A truck driver starts of with his loaded truck, What are the major energy changes that take place in setting the truck into motion?[3]
(c) A glass jar contains a liquid of density 'd' up to a height 'h' at a place where acceleration due to gravity is 'g' and the atmospheric pressure is 'pa'. [4]
- What is the pressure at the free surface of the liquid?
- Write an expression for the total pressure at the base of the jar.
- ) What will be the lateral pressure at this depth on the inner side of the jar?
Question 3
(a) [4]
- State three characteristics of a musical sound.
- How does the musical sound differ from noise?
(b) [4]
- How does a stretched string on being set into vibration, produce the audible sound?
- Will the sound be audible if the string is set into vibration on the surface of the moon? Give reason for your answer.
(c) [4]
Radio waves of speed 3 × 108 m/s are reflected of the moon and received back on earth, the time elapsed between the sending of the signal and receiving it back at the earth surface is 2.5 seconds, What is the distance of the moon from the earth?
Question 4
(a) The diagram alongside shows the path of a ray of light through a rectangular
glass block placed in a liquid of uniform density. [3]
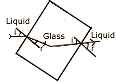
- Does the light speed up or slow down in glass?
- )Give reasons for your answer.
(b) What is the angular deviation of the emergent ray from the glass block with respect to the incident ray? [1]
(c) Show with the help of ray diagram, the path of the ray when incident normally on the first surface of the glass block, through the block and the liquid. [2]
(d) What should be the ratio of the speed of light through the liquid to the speed through glass so that there is no refraction of light at the boundaries of the glass block when the system is illuminated by light of one colour. [1]
(e) [3]
- State the equation for the relation between the frequency and wave length of light in vacuum.
- What is the relation between the angle of incidence 'i' in the liquid and the angle of refraction 'r' in the glass?
Question 5
(a) In a laboratory experiment to measure specific heat capacity of copper, 0.02
kg. of water at 700C was poured into a copper calorimeter with a
stirrer of mass 0.l6 kg, initially at 150C. After stirring, the final
temperature reached to 450C. Specific heat of water is taken as 4200
J/kg0C. [6]
- What is the quantity of heat released per kg of water per 10C fall in temperature?
- Calculate the heat energy released by water in the experiment in cooling from 700 to 450C.
- Assuming that the heat released by water is entirely used to raise the temperature of calorimeter from 150C to 450C, Calculate the specific heat capacity of copper.
(b) Define the e.m.f (E) of a cell and the potential difference (V) across a resistor (R) in terms of the work done in moving a unit charge. State the relation between these two works and the work done in moving a unit charge through a cell connected across the resistor. Take the internal resistance of the cell as 'r'. Hence obtain expression for the current 'i' in the circuit. [4]
Question 6
(a) A bulb is marked 100 W, 220 V and an electric heater is marked 2000 W, 220
V. [5]
- What is the ratio between the resistances of these two devices?
- How does the power-voltage rating of a device help us to decide about the type of leads (connecting wires) to be used for it?
- In which of the two devices, a thicker connecting wire or lead is required?
(b) Draw a representative diagram of a dc motor. Label the following in your diagram: [5]
- The field magnet
- The armature
- Commutators
- Wire brushes
What is the energy change in this case?
Question 7
(a) The following diagram is the simplified version of an electrode gun which is
an integral part of a cathode ray-tube. 'A' is a metal cylinder. [5]
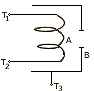
- Copy the diagram in your answer book. Draw a pair of planets P1 and P2 to apply electric field, a screen S and an enclosure.
- What are the functions of A, B, P1 and P2.
(b) 27 Mg β Al Y
12 --> -->
In the above nuclear reaction. [3]
- 27Mg12 emits α, β-particle and is transformed to aluminium. What is the mass number and the atomic number of aluminium.
- Aluminium emits γ ray. What is the resulting nucleus?
(c) [2]
- Which radiation or particle from radioactivity produces maximum biological damage?
- State three precautions that must be taken while handling a radio active source.